Unleashing the Power of Self-Motivation: A Guide to Ignite Your Drive
Self-motivation is the inner drive, persistence, and resilience that propels people toward their goals and dreams. It is the inherent force that drives someone to act, persevere in the face of adversity, and remain devoted to their goals. Self-motivation, as opposed to external motivators (such as prizes or peer pressure), develops from inside, fueled by own desires, beliefs, and passions. It is the engine that pulls people onward even when they face hurdles or disappointments.

Self-Motivation in Personal Growth Importance
Self-motivation is the bedrock of personal growth and development. Here’s why it’s so important:
- Empowerment
Individuals that are self-motivated feel empowered to take charge of their lives. They have faith in their abilities, which makes them more proactive and resilient in pursuing their goals.
- Resilience
Self-motivated people are more resilient in the face of hardship. They recover from failures, setbacks, or problems by resolving to learn and improve.
- Goal Attainment
Setting and accomplishing objectives requires self-motivation. It offers the impetus needed to pursue long-term goals, promoting a sense of accomplishment and fulfillment upon completion.
- Constant Improvement
Self-motivated people are more inclined to improve themselves. They actively seek opportunities for learning and development, continually seeking to improve their skills and knowledge.
- Positive Mindset
Self-motivation fosters a positive attitude. It encourages people to focus on opportunities rather than problems, cultivating a positive attitude that propels them forward even in the face of hardship.
- Adaptability
Self-motivation enables individuals to adapt in quickly changing settings. They are more adaptable, perceiving new challenges as chances for progress rather than obstacles.
- Leadership and Influence
Self-motivated people are frequently catalysts for encouraging others. Their zeal and determination act as a beacon, inspiring and influencing everyone around them.
Understanding the nature of self-motivation offers the groundwork for individuals to effectively harness and channel this internal power toward personal progress, achievement, and success in all aspects of life.
Understanding Self-Motivation
Psychological Framework: Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Motivation
- Intrinsic Motivation: Intrinsic motivation, which stems from internal drives, entails engaging in tasks for the intrinsic satisfaction they provide. Individuals who are driven by intrinsic motivation derive joy, contentment, and personal gratification from the process rather than from external rewards or accolades. Pursuing a pastime, learning a new skill out of genuine curiosity, or tackling a problem for the sake of the challenge it brings are all examples.
- Extrinsic Motivation: Extrinsic motivation, on the other hand, is the result of external incentives or pressures. It entails participating in activities in order to obtain external rewards, avoid punishment, or meet external expectations. Working for a salary, seeking praise or credit, or completing deadlines due to external consequences rather than personal interest are common examples.
Understanding the interaction of these two motivating impulses is critical for efficiently harnessing self-motivation. While external rewards can motivate people to act, aligning activities with internal motivations is typically necessary for long-term commitment and fulfillment.
Factors Influencing Self-Motivation
- Mindset: An individual’s thinking has a huge impact on their self-motivation. A growth mindset encourages resilience and long-term drive by trusting in one’s ability to learn and improve. A fixed attitude, which believes abilities are static, may stifle motivation.
- Goals: Clear, relevant, and attainable goals are effective motivators. Setting goals that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) provides direction and purpose, which fuels motivation.
- Environment: Social circles, job dynamics, and physical locations all have an impact on self-motivation. Environments that foster growth, provide resources, and provide positive reinforcement boost motivation.
- Self-Efficacy and Beliefs: Self-belief and confidence in one’s own talents (self-efficacy) are critical components of self-motivation. Individuals who have stronger self-efficacy are more inclined to set lofty objectives and persevere in the face of adversity.
- Autonomy and Control: Having autonomy and control over one’s actions and decisions develops a sense of ownership, which leads to higher self-motivation. Feeling in control allows people to focus their efforts on attaining their goals.
- Emotional Well-being: Motivation is greatly influenced by one’s emotional condition. Positive emotions can boost motivation, whilst negative emotions like worry or anxiety can derail it. Practices that promote emotional balance can help to keep motivation levels high.
Individuals can examine their own motivational drives, harness strengths, and build ways to improve self-motivation for optimal performance and personal fulfillment by recognizing and understanding these elements.
The Science Behind Motivation
Neurological Basis of Motivation
- Dopaminergic Pathways: Dopamine, a neurotransmitter, is essential for motivation. It is linked to the brain’s reward system, namely the mesolimbic circuit. Dopamine levels rise when people anticipate or experience pleasurable or rewarding stimuli, reinforcing actions and pushing people to seek comparable rewards.
- Prefrontal Cortex and Motivation: Motivation is influenced by the prefrontal cortex, which is engaged in decision-making and goal-directed behavior. It assists individuals in weighing options, planning, and carrying out actions required to accomplish desired objectives.
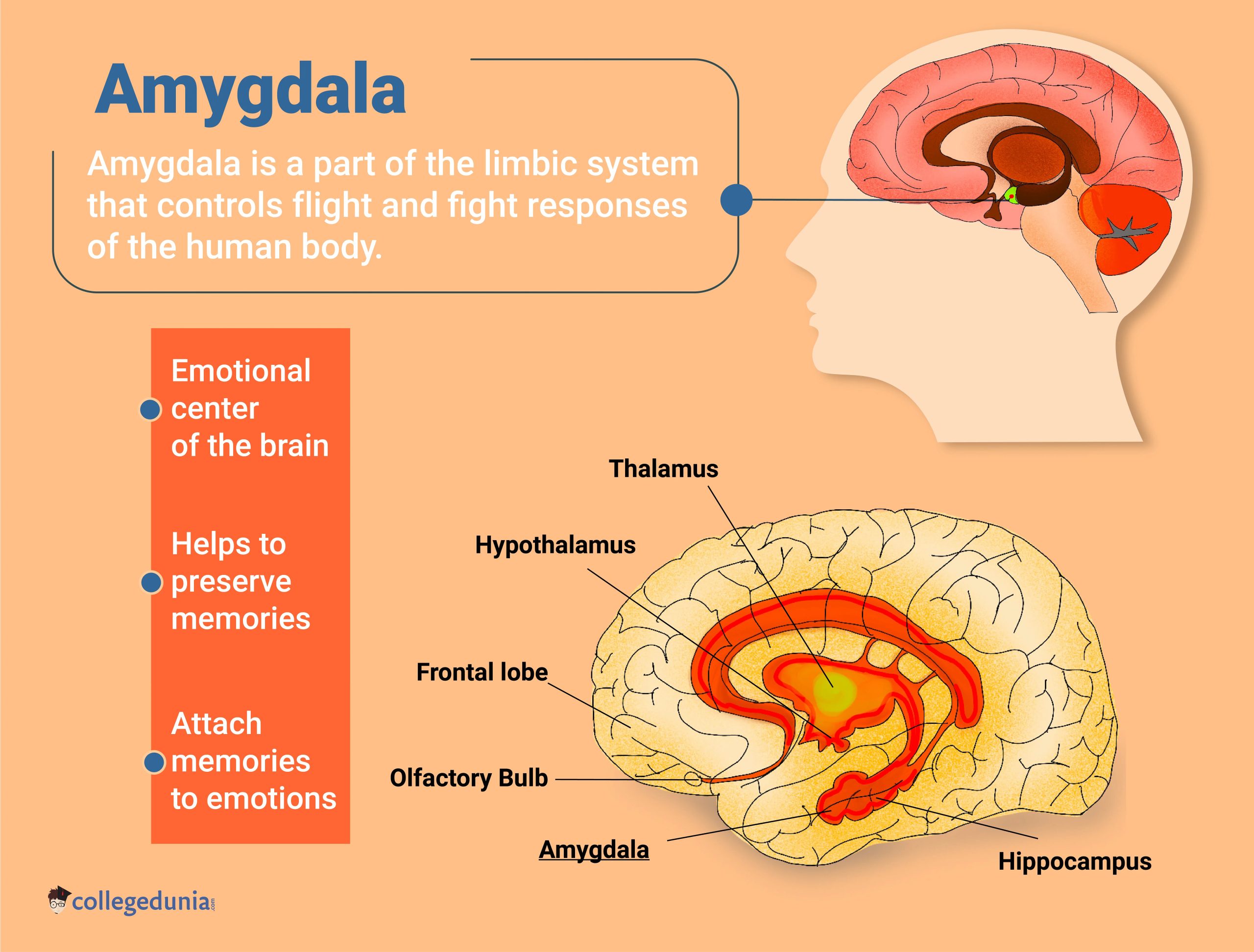
- The Role of the Amygdala: The limbic system’s amygdala processes emotions and influences motivation. It aids in the association of emotions with specific stimuli, influencing motivation based on emotional reactions.
- Neuroplasticity and Motivation: Motivation is aided by neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to rearrange and develop new neural connections. Learning and adapting to new actions or goals cause changes in brain circuits, which influence motivation as people advance.
Hormonal Impact on Motivation and Drive
- Dopamine and Motivation: Dopamine controls not only the brain’s reward system but also motivation. It is linked to goal-directed conduct and the desire to obtain incentives or desired outcomes.
- Serotonin and Motivation: Another neurotransmitter that modulates mood and emotional states is serotonin. It has an impact on motivation because of how it affects an individual’s sense of well-being, which influences their drive and tenacity.
- Cortisol and Stress: Cortisol, the stress hormone, can have an impact on motivation. Cortisol levels that are elevated as a result of prolonged stress may depress motivation, significantly influencing decision-making and goal pursuit.
- Testosterone and Motivation: Testosterone, best known for its involvement in male reproductive activities, also has an impact on motivation. It can influence motivational levels by increasing desire, ambition, and competition.
Understanding the neurological and hormonal systems behind motivation helps us understand how the brain processes information, responds to stimuli, and influences behavior. This understanding can assist individuals in optimizing their settings and behaviors in order to increase motivation and accomplish desired outcomes.
Techniques to Boost Self-Motivation
Setting Clear Goals
- SMART Goals and Their Impact: SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) provide clarity and direction. They divide goals down into manageable steps, making them more attainable and motivating.
- Importance of Goal Setting in Motivation: Clear goals provide a path for motivation by creating a sense of purpose and accomplishment. They serve as milestones, helping people to track their progress and keep focused on their goals.

Overcoming Procrastination
- Approaches to Combat Procrastination: Tasks can be broken down into smaller, more manageable parts to assist overcome the overload that leads to procrastination. Setting deadlines, prioritizing work, and addressing the most difficult chores first can all help to enhance motivation.
- Productivity Techniques: Working in focused intervals with brief pauses, such as the Pomodoro Technique, can boost productivity and motivation. Work divided into intervals improves concentration and decreases the desire to procrastinate.
Cultivating a Positive Mindset
- Power of Positive Thinking:Adopting a good mindset increases resilience and motivation. It entails changing negative ideas into positive ones, focusing on solutions rather than Problems, and cultivating thankfulness.

- Mindfulness and Motivation: Meditation and being present in the moment are two mindfulness activities that promote self-awareness and alleviate stress. They improve focus and clarity of thought, which boosts motivation.
Building Self-Discipline
- Habits and Routines for Self-Discipline: Creating regular routines and habits helps to reinforce self-discipline. Discipline is developed by consistently executing duties at set times, making it simpler to stay motivated and concentrated.
- Accountability and Consistency: Accountability to oneself or others, whether through goal setting, recording progress, or having an accountability partner, promotes consistency. It strengthens devotion and aids in motivation even during difficult circumstances.
Using these approaches creates an environment that encourages self-motivation. They give people the tools they need to set clear goals, overcome obstacles like procrastination, keep a positive attitude, and develop the discipline required to stay motivated toward their goals.
Strategies for Sustaining Motivation
Seeking Inspiration and Role Models
- Learning from Inspirational Figures: The journeys of inspirational people reveal insights into their tenacity, perseverance, and success tactics. Their stories can inspire people and teach them crucial lessons.
- How Role Models Drive Self-Motivation: Role models provide inspiration and direction. Observing their accomplishments, work ethics, and approaches to overcoming obstacles can inspire and motivate one’s own ambition and aspirations.
Handling Setbacks and Failures
- Resilience and Adaptability in Motivation: Individuals with resilience are able to recover from setbacks. Accepting failure as a learning opportunity promotes adaptation and resilience, which are critical components in maintaining motivation.
- Learning from Failures to Fuel Motivation: Failure analysis enables in the extraction of lessons, allowing individuals to pivot, modify strategy, and grow. Setbacks are transformed into stepping stones for future success, resulting in renewed enthusiasm.
Self-Care and Well-being
- Connection Between Physical Health and Motivation: Physical health has a big impact on motivation. Regular exercise, appropriate sleep, and a well-balanced diet all lead to greater energy and mental clarity, which improves motivation.
- Mental Health Practices for Sustained Motivation: Mindfulness, stress management, and getting help when required all contribute to mental well-being. A healthy mind encourages resilience, optimism, and long-term motivation.
Adopting these tactics provides individuals with the tools they need to maintain and sustain motivation over time. Individuals build their inner drive and resilience by seeking inspiration, learning from setbacks, and emphasizing self-care, assuring continuing progress toward their goals.
Real-life Success Stories
These people’s experiences demonstrate the transformational power of self-motivation. Their unrelenting determination, resilience, and belief in their aims not only propelled them to amazing successes, but also encouraged countless others to pursue their aspirations in the face of adversity.
- Oprah Winfrey: Oprah Winfrey rose from a difficult beginning defined by poverty and suffering to become one of the most influential television figures. Her unrelenting self-motivation, perseverance, and determination enabled her to build a global media empire that has inspired millions.
- Elon Musk: Elon Musk, the creative entrepreneur behind firms such as SpaceX and Tesla, symbolizes unwavering self-motivation. Despite multiple setbacks and criticisms, his ambition to revolutionize space exploration and renewable energy originated from an unwavering belief in his ideals.
- K. Rowling: J.K. Rowling encountered personal challenges before gaining enormous success with the Harry Potter series, including financial difficulty and rejections from publishers. Her self-motivation and passion to narrative propelled her forward, resulting in the creation of a literary phenomenon and the inspiration of countless young readers.
- Serena Williams: Serena Williams, the renowned tennis player, exhibits self-motivation via her passion to the sport. Despite difficulties and critics, she maintained a passionate devotion to perfection, becoming one of tennis’ best athletes.
- Stephen Hawking: Stephen Hawking’s incredible achievements to science are proof of his unwavering self-motivation. Despite suffering from a crippling illness, his intense curiosity, determination, and love for solving the secrets of the universe resulted in ground-breaking breakthroughs in theoretical physics.
- Malala Yousafzai: Malala Yousafzai, a Nobel laureate and advocate for girls’ education, demonstrated tremendous self-motivation in the face of adversity. Despite surviving a Taliban assassination attempt, she persisted in her work, becoming a global symbol of courage and empowerment for education.
The Role of External Support
The Influence of Support Networks and Communities on Motivation
- Emotional Support: During difficult circumstances, support networks and communities provide emotional support by offering encouragement, empathy, and understanding. This improvement in emotional well-being has a favorable effect on motivation, creating confidence and resilience.
- Accountability and Encouragement: Participating in a supportive network encourages accountability. Communities or groups that have common aims or interests provide encouragement, accountability, and shared experiences, promoting motivation via shared accomplishments and challenges.
- Resource Sharing and Learning: Support groups are frequently used as forums for information sharing. They provide resources, assistance, and knowledge, thereby shortening learning curves and broadening viewpoints. This flood of knowledge can drive people by providing new insights and strategies.
Seeking Help When Required

- Recognizing Limitations: Recognizing one’s limitations and asking assistance shows self-awareness and strength rather than weakness. It is critical to recognize when outside aid can bring significant insights or assistance.
- Utilizing Expertise and Guidance: Seeking assistance, experience, and insight from mentors, coaches, or professionals in relevant industries might help. When faced with problems or uncertainties, their input can bring clarity, direction, and renewed motivation.
- Building a Support System: Building a support network entails cultivating ties with mentors, peers, or support groups. Engaging with a diversified network provides a variety of perspectives and multifaceted support, boosting motivation in various parts of life.
External support serves as a catalyst, increasing an individual’s self-motivation by giving opportunities for improvement, encouragement during difficult times, and learning tools. Knowing when to seek help and connecting with supportive networks can considerably aid with long-term motivation and personal development.
Conclusion
Personal growth, achievement, and resilience are all driven by self-motivation. Several major aspects have surfaced during this investigation:
Key Points
- Definition and Importance: Self-motivation arises from internal aspirations and is essential for human development, resilience, and goal achievement.
- Understanding Self-Motivation: Understanding the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation, as well as the elements that influence motivation, is the foundation for effectively harnessing this inner drive.
- The Science Behind Motivation: Investigating the neurological and hormonal elements of motivation gives light on how the brain functions and responds to stimuli.
- Techniques to Boost Self-Motivation: Different ways enable individuals to fuel their drive, from goal planning and overcoming procrastination to cultivating a positive mindset and developing self-discipline.
- Strategies for Sustaining Motivation: Seeking inspiration, dealing with disappointments, and prioritizing self-care all help to keep motivated during life’s ups and downs.
- The Role of External Support: Recognizing the importance of supportive networks and knowing when to seek aid complements and enhances self-motivation.
- Encouraging Action and Implementation: The path to long-term self-motivation does not end with comprehension; it begins with application. It is critical to actively employ these techniques:
- Set Clear Goals: Create specific, attainable goals that are in line with your personal goals.
- Adopt Tactics: Through constant activity, you may overcome procrastination, create a good mindset, and cultivate self-discipline.
- Embrace Support: Create and utilize supportive networks, seeking help when necessary to supplement self-motivation.
Individuals can harness the power of self-motivation to manage problems, achieve objectives, and lead a satisfying life by taking persistent measures to implement these tactics and seeking continual growth. Remember that self-motivation is a talent that can be developed and polished over time, leading to personal growth and accomplishment.

